7th April 2020 • Sticky Post
Codependency, and how it impacts your life
“A codependent person is one who has let another person’s behaviour affect him or her, and who is obsessed with controlling that person’s behaviour.” -Melody Beattie, author of ‘Codependent No More.’
Defining Co-dependency
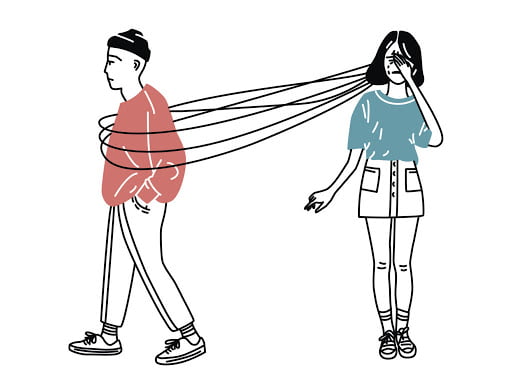
Most psychologists view codependency as a product of two dysfunctional personalities coming together to an extent where boundaries between the personalities cease to exist. Psychologists call this process “enmeshment.” We all know deeply unhappy couples who have stayed together in spite of the misery they create. And while there are many reasons for couples to stick together in dire situations (children, finances, inertia, loyalty, etc.), the main reason people stay in these relationships is the belief of one partner (or sometimes both) that they deserve to be mistreated.
Traditionally, codependent relationships have been defined by control. Studies from the late 1980s and early 1990s concluded that codependent individuals based their lives, self-esteem and sense of well-being on the behaviour of an unhealthy family member. They concluded that a pattern was established with the functional partner nurturing the afflicted partner, and creating a pleasurable and self-reinforcing cycle which rewarded misbehaviour. As the psychologist Reevah Simon has noted, “wherever there is ongoing conflict, there is underlying agreement.” In other words, the functional partner consents to the pattern of codependency, and takes a sense of pleasure, satisfaction, or purpose from it.
Codependency in the Family
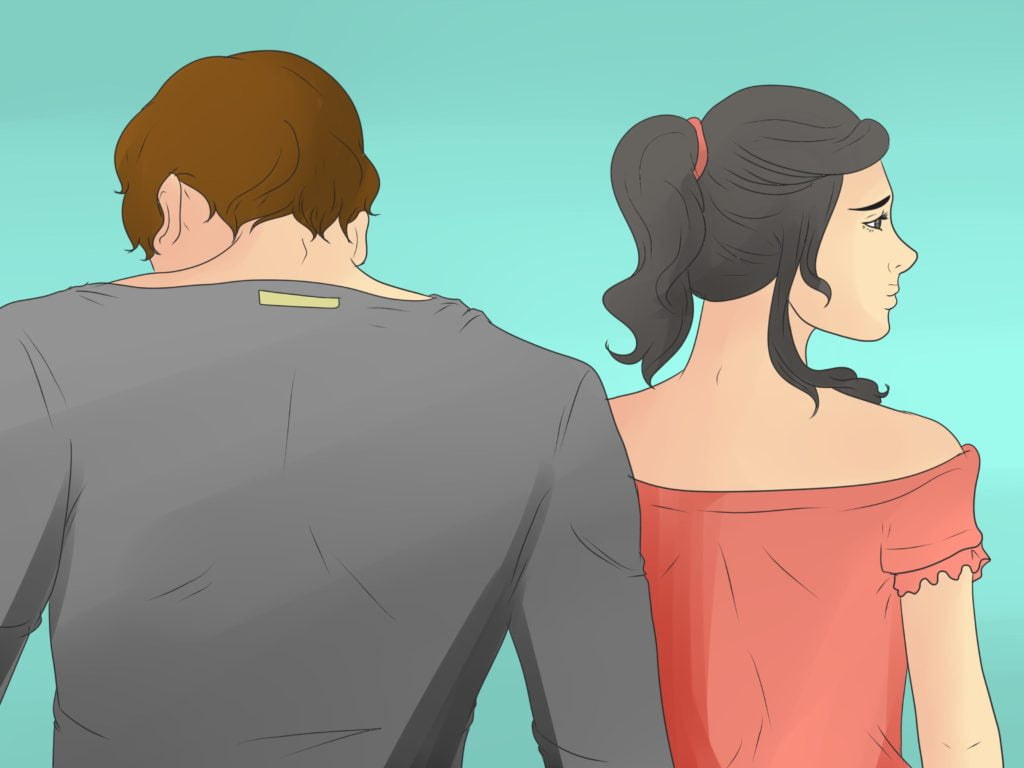

The classic example of a codependent relationship is the enabling wife of an alcoholic, but over time the definition has expanded to include partners of individuals with any addiction or chemical dependency, partners of some individuals afflicted by chronic physical or mental illnesses, and any member of a dysfunctional family with symptoms of the disorder.
If you grew up in a dysfunctional family, you are at a far greater risk of developing codependent relationships. According to Mental Health America, members of dysfunctional families are used to denying the existence of problems. They don’t talk about them or confront them, so family members learn at a young age to repress difficult emotions and deny their own needs: “They develop behaviours that help them deny, ignore, or avoid difficult emotions. They detach themselves. They don’t talk. They don’t touch. They don’t confront. They don’t feel. They don’t trust. The identity and emotional development of the members of a dysfunctional family are often inhibited.”
Members of dysfunctional families are programmed from an early age to shift their energy and focus from themselves to the family member who is ill or addicted. They place the needs of the afflicted family member above their own in order to keep the family unit intact. As a result they often lose their sense of self. They develop a pattern of putting the well-being of a loved one ahead of their own, and become disconnected from their own needs and desires, and this pattern is primed to repeat itself in adult life.
Are You in A Co-dependent Relationship?

People suffering from codependency generally have low self-esteem and look for things outside of themselves for validation and fulfillment. They have difficulty “being themselves” and are prone to addictive or compulsive behavioural disorders. They generally have good intentions and try to take on the role of caregiver in many of their relationships, but often become self-defeating and compulsive in the role, enabling or shrugging off unacceptable behaviour.
This creates a cycle where the person needing care becomes ever-more dependent on their caregiver, while avoiding the consequences of their destructive behaviour. Meanwhile, the caregiver becomes habituated to the sense of satisfaction and fulfillment they derive from being needed. Eventually, the caretaking becomes a compulsion, and the caretaker develops a sense of martyrdom and victimhood, but is unable to break away from the mutually destructive relationship. This leads to feelings of helplessness and depression.
A Google search will yield a plethora of questionnaires designed to identify signs of the disorder, but please note that only a qualified professional is capable of making a diagnosis. The lists frequently include questions asking about your ability to communicate negative emotions, your tolerance towards living with toxic relationships, your self-esteem, and your ability to ask for, and deny requests for help. If you’re worried that you might be trapped in a cycle of co-dependence, we’d recommend trying this online questionnaire, and if the results indicate that you may be afflicted, seek out a mental health professional immediately.
Treating Codependency
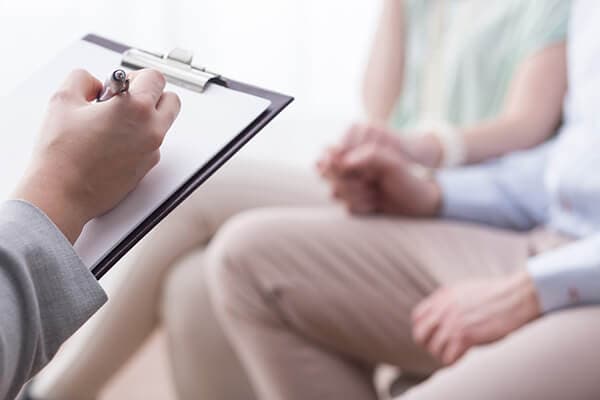

If you’re convinced you suffer from this disorder, we’d recommend starting with a diagnosis, counseling, and peer-support fellowships. Al-Anon and Nar-Anon are both fantastic resources and support systems which will let you access the support and wisdom of those who have overcome codependence. SMART Recovery takes an approach to addiction based on the principles of Cognitive Behavioural Therapy, and their support program for family members emphasizes positive and honest communication for guiding addicted partners and family members toward healthier lives, and avoiding the pitfalls of codependence. Traditional therapy and CBT have also helped many codependent partners and family members to take control of their own lives and well-being.
Non-traditional cures can also be used to combat codependency. Mindfulness practice is a great way to connect with yourself and explore your own thoughts, needs, and desires. Yoga can also help center you and connect body, mind, and soul in a way that will help you actualize your own will to take control of your life. And treatment with psychedelics and ibogaine have also proved effective in helping patients confront traumatic aspects of their pasts, and deal with painful memories and emotions. Addiction can ruin the lives of addicts and their loved ones. Don’t let it ruin yours.


